MCE for Critical Controls
How My Competency Expert (MCE) Supports the ICMM Critical Control Management Framework
MCE closes the biggest gap in Critical Control Management — the human‑performance gap — by ensuring that the right people, with the right competencies, are in the right roles, with verifiable evidence.
Companies adopting the ICMM Critical Control Management (CCM) framework face a common challenge: ensuring that critical controls do not fail due to gaps in human performance. Many catastrophic or high‑potential incidents are not caused by technical system failures, but by people lacking the required knowledge, skills, experience, or clarity of accountability to operate, verify, or oversee critical controls effectively.
My Competency Expert (MCE) directly addresses this challenge by providing a single, structured, and auditable system that links critical controls to the competencies and experience of the people responsible for them. MCE strengthens CCM implementation by ensuring that every critical control is backed by competent, verified, and accountable individuals.
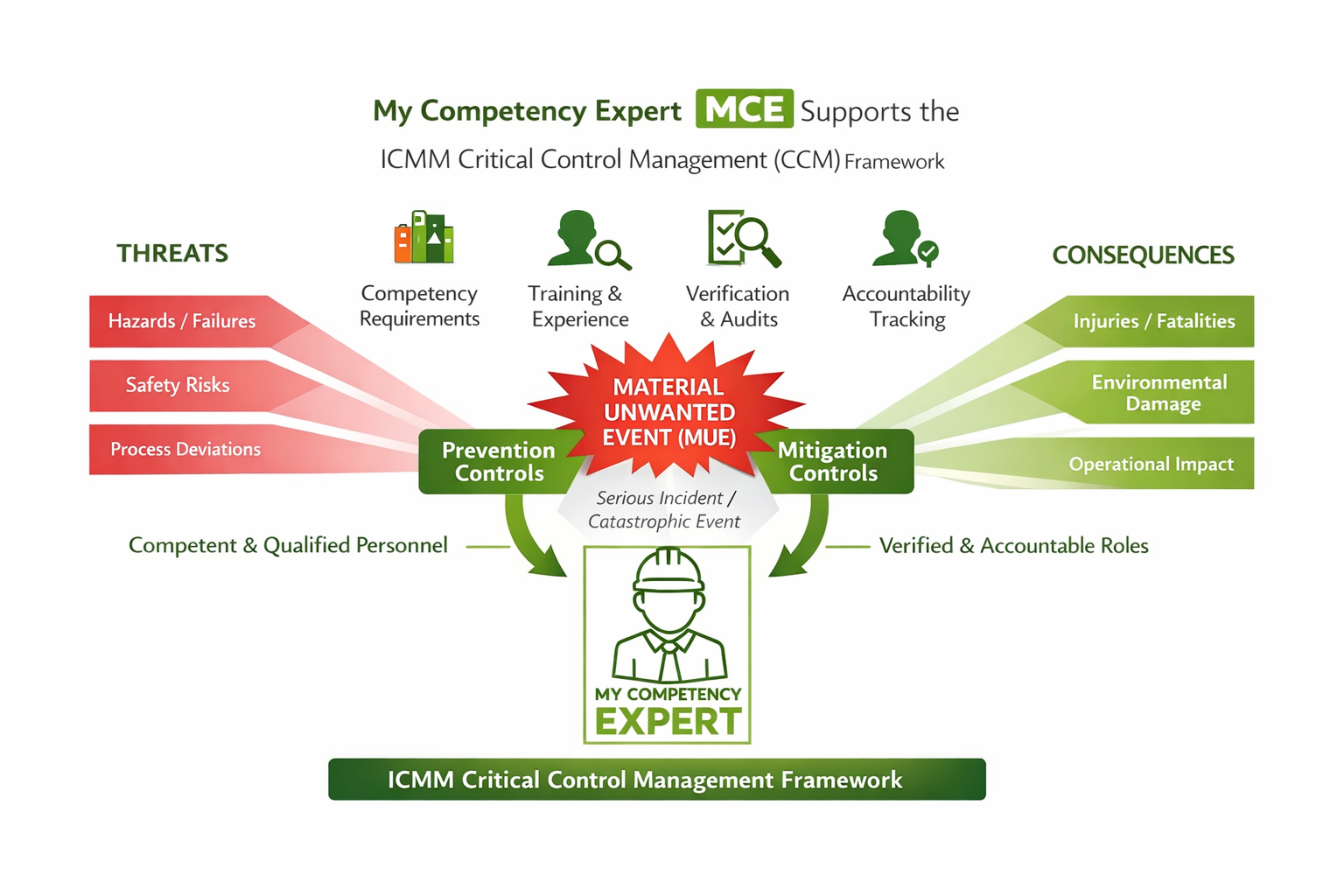
ABOVE: My Competency Expert supports the ICMM Critical Control Management framework at every step.
MCE defines and monitors:
Competency Requirements - defined and mapped to Material Unwanted Events, ensuring each role has clearly identified capability requirements.
Training & Experience – provides evidence‑based assurance of human performance, including assessments, TREx experience records, and currency of competency.
Support verification and audit processes through dashboards and reporting that show the competency health of critical controls in real time.
Accountability Tracking through Letters of Appointment, SME delegation, and transparent management-structure role mapping.
By closing the human‑performance gap, MCE transforms critical control intent into reliable execution. It equips leaders with clear visibility of whether critical controls are truly effective—because the people responsible for them are demonstrably competent. This makes MCE an essential enabler for any mining operation striving to meet Critical Control Management good practice and achieve stronger, more defensible critical control assurance.
ABOVE: MCE provides the process to ensure the right people with the right competencies are in the right roles.
Background
The ICMM Critical Control Management (CCM) Good Practice Guide provides a structured, leading-practice approach to managing the most important barriers that prevent or mitigate Material Unwanted Events (MUEs) — rare but potentially catastrophic incidents causing serious injury, fatality, or major disruption.
At its core, CCM involves:
Identifying priority risks and the critical few controls (often via bowtie analysis) essential to preventing/limiting MUEs.
Defining clear performance standards for each critical control.
Assigning explicit accountability.
Implementing rigorous verification and monitoring to confirm controls function as intended.
Effective CCM recognises that many critical controls depend on human performance — execution, supervision, maintenance, or oversight. Human-factor failures (gaps in knowledge, skills, experience, or discipline) often appear in investigations. ICMM stresses robust assurance of competency for roles tied to critical controls.
MCE supports this by focusing on competency assurance within the Management Structure — the layer responsible for designing, implementing, sustaining, and improving critical control systems.
Specifically, MCE enables:
Mapping competencies to Material Unwanted Events — Linking Management Structure roles to controls/PHMPs they own, operate, supervise, or verify, including senior competencies for PHMP establishment, review, and improvement.
Assuring human performance — Tracking competencies at all levels with Time-Based Recoird of Experience (“TREx”) for experience evidence, assessments, and verifications.
Supporting verification — Recording human-element checks (e.g., competency for PHMP development / updates) to bolster CCM programs.
Auditable reporting — Dashboards linking competency health to critical controls/MUE prevention for reviews and audits.
Allocating the correct competencies
My Competency Expert is built around the concept of a “hierarchy of competency” – that is, recognising that there are many ways to achieve competency – not only classroom-based teaching.
One of the core tasks undertaken by MCE in supporting the CCM process is allocating the correct competencies to each role that is given a task relating to this process. MCE does this by accessing its’ proprietary reference library which has been built up with our clients over many years. It includes a mix of delivery methods, including:
· Non-accredited ticket / Certificate of Completion
· Time-based Record of Experience (“TREx”)
· Certificate of Competency / License – often issued by an industry authority
· Verification of Competency (VoC), mapped to a unit, issued by a Subject Matter Expert
· Statement of Attainment issued by a Registered Training Organisation (RTO)
· Full Qualification issued by a University / College
MCE builds these mappings directly, linking Management Structure to CCM bowties for defined, tracked, and verified competencies across mining types. Relevant RII units (from training.gov.au) can be imported/configured in MCE as part of role competency profiles, with evidence linked to certs, assessments, or on-the-job records via TREx.
These concise mappings create clear, auditable links between roles, critical controls, and competency assurance — with controls grouped under their respective MUE and senior roles tied to relevant RII qualifications/units for Australian mining compliance.
Verification Activities
My Competency Expert aids this framework by providing an auditable verification process, including:
· TREx records
· competency expiry / refresher
· Link to Learning Management System
· Review Records
· Compliance Reporting
· Letter of Appointment
· Competency Gap Plan
· Delegation to Subject Matter Expert
The inclusion of a signed Letter of Appointment in MCE's evidence tracking provides formal, auditable proof of role delegation and accountability, aligning with regulatory expectations for management structures.
Conclusion
By embedding this competency focus, MCE fills a common CCM gap: proactive management and verification of human-dependent aspects of critical controls, from leadership frameworks to operational execution.
This makes MCE a practical tool for any mining operation pursuing ICMM CCM goals, strengthening critical control effectiveness through evidence-based competency assurance.
If you are a mine operator seeking to improve role definition, competency management, and critical control assurance, MCE offers a proven platform adaptable to your regulatory and site context.
We welcome the opportunity to discuss a tailored pilot or demonstration. Please contact us to explore how MCE can deliver stronger, auditable risk management aligned with ICMM leading practice.